Professor Sun Genban' s Team from the College of Chemistry Published Research Findings in Angewandte Chemie International Edition
Recently, Professor Genban Sun’s research team from the College of Chemistry at Beijing Normal University published their latest research findings in the international chemistry journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition. The study offers novel insights into the design of advanced Li-O2 battery systems and the enhancement of their performance.

The abstract of the paper is as follows:
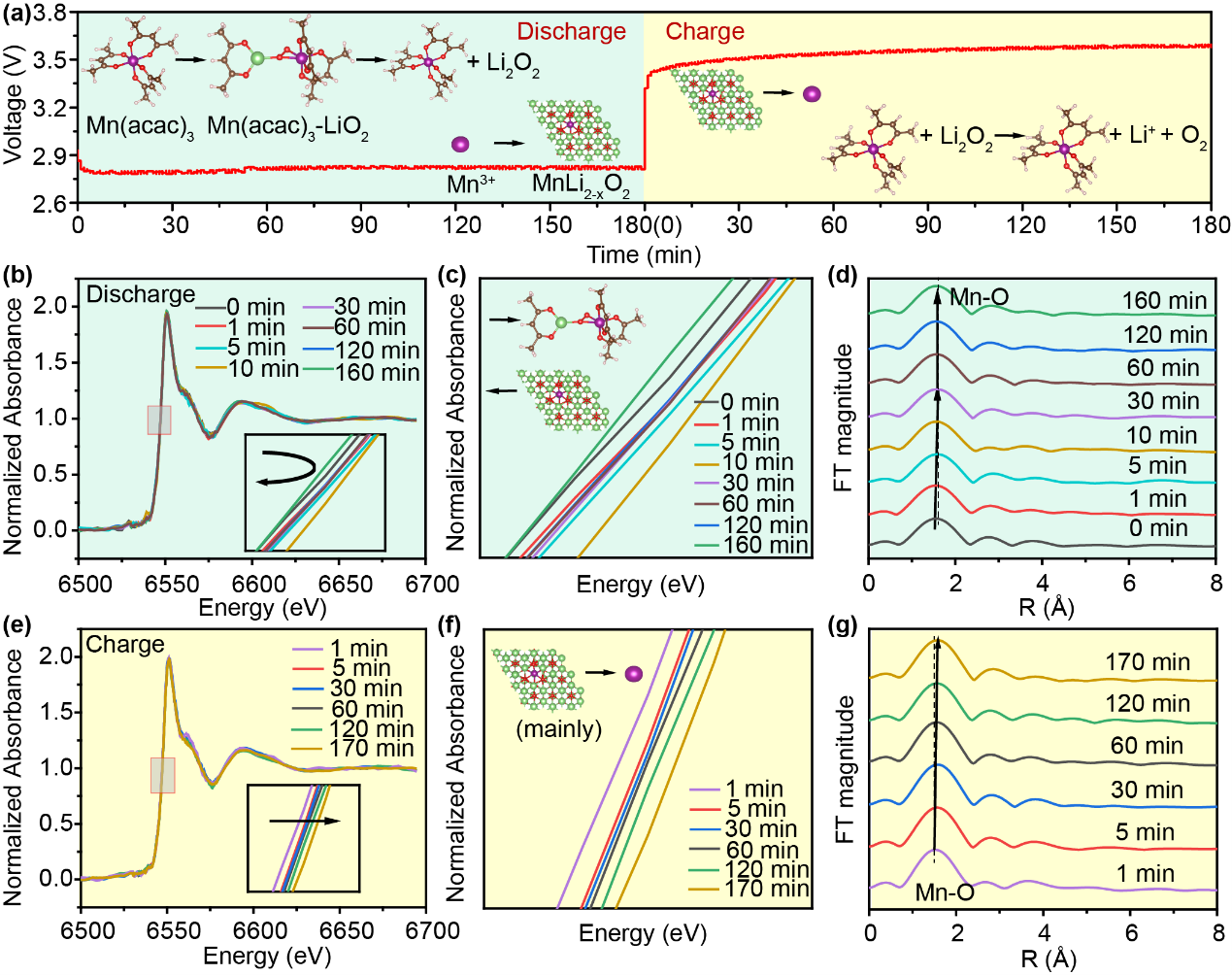
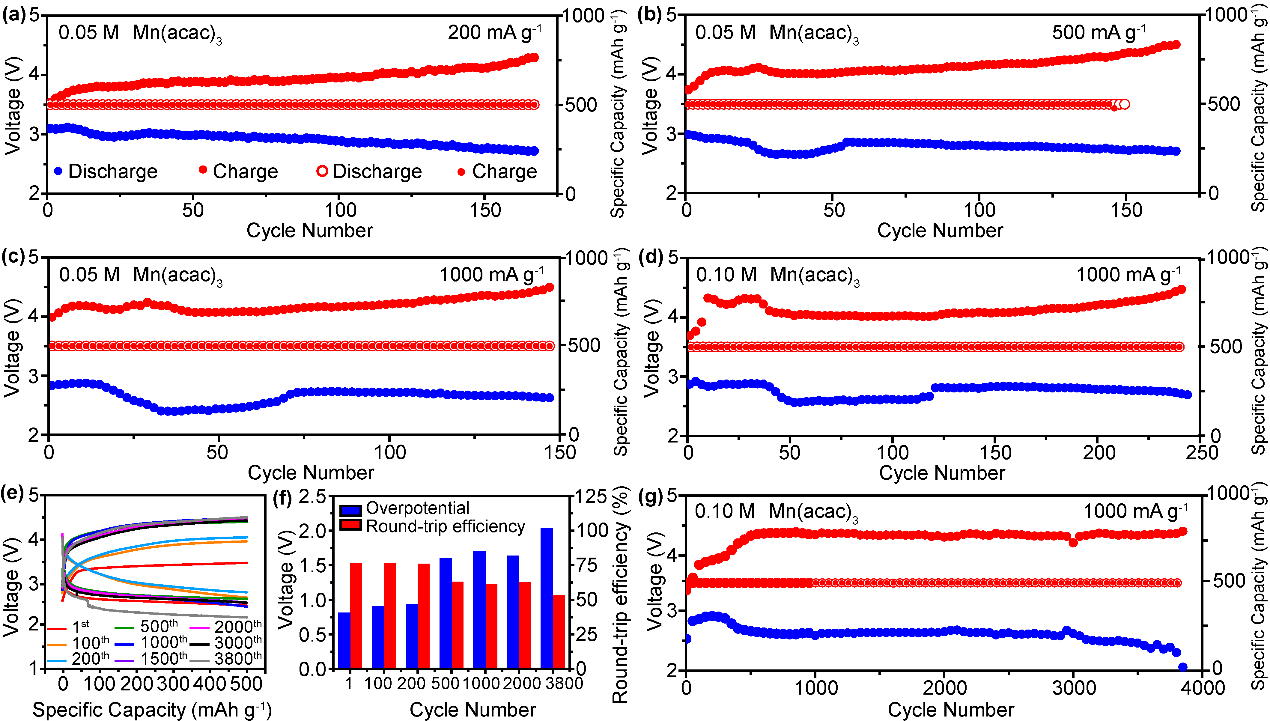
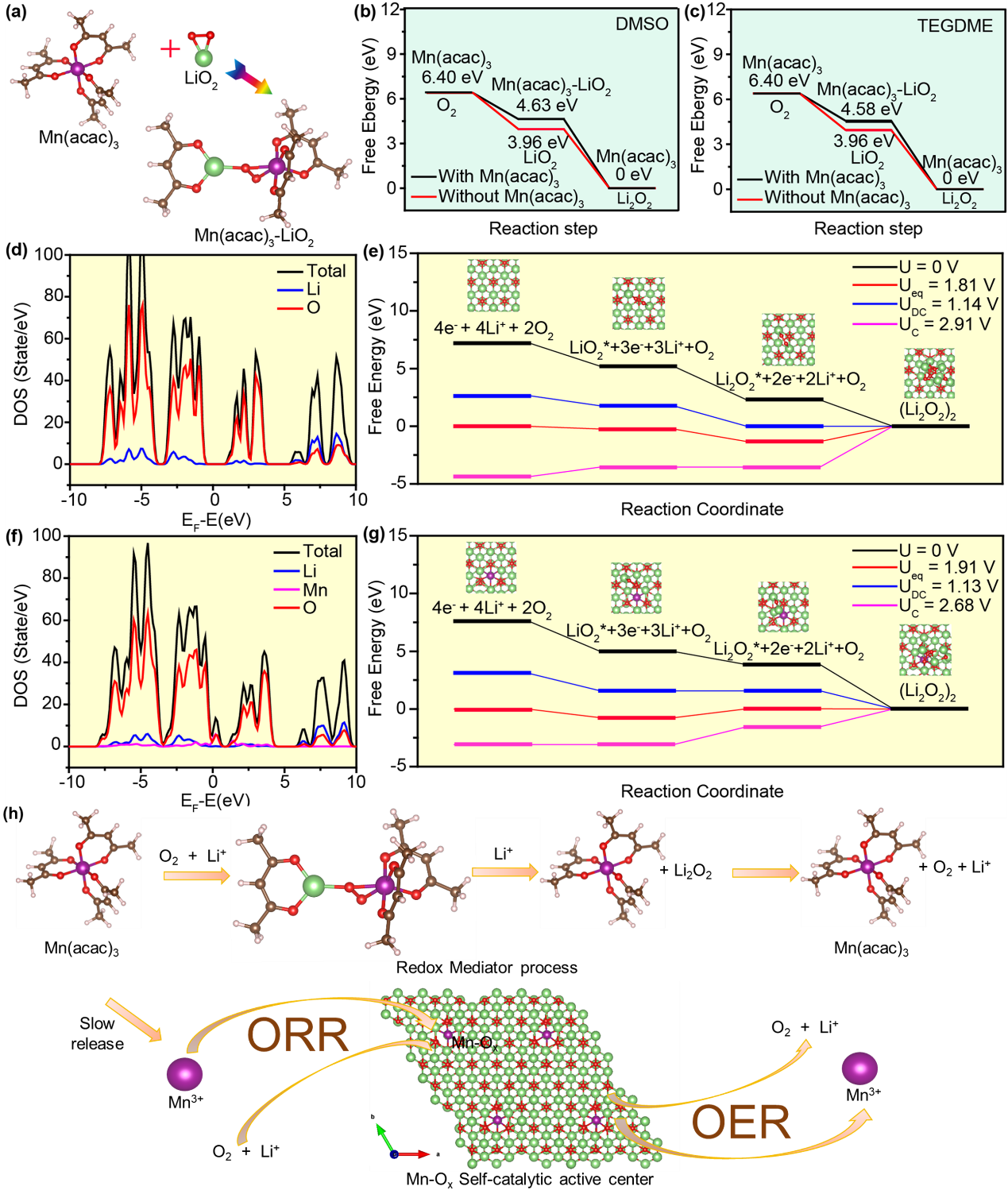
The sluggish kinetics of Li-O2 batteries significantly limit their performance. To address this issue, the insulating characteristics of the discharge product Li2O2 and the reactivity of highly active superoxide species are examined. Herein, organic metal salts with weak electrolyte properties are utilized as bifunctional additives. The ionized metal ions can be reduced and doped Li2O2 through in situ electrochemical implantation, thereby altering its insulating properties. Additionally, organic metal salts function as redox mediators (RMs), stabilizing the intermediate Li-O2 and facilitating its further disproportionation to Li2O2, as well as enhancing the decomposition reaction during charging, which are further proven by the in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy and UV–vis spectroscopy. Notably, Li-O2 batteries incorporating Mn(acac)3 demonstrate an ultra-low overpotential of 0.43 V and sustain 250 long cycles at 1000 mA g−1. Furthermore, when combined with the optimized cathode, a remarkable cycle stability of 3850 cycles at 1000 mA g−1 is achieved. These findings offer novel insights into the design of advanced Li-O2 battery systems and the enhancement of their performance.
Reference:
Zheng, X.; Yuan, M.; Su, P.; Kong, Q.; Xu, J.; Sun, G. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, e202504554.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202504554?msockid=120a3b18569a68f50e6e296757fc69c0


